| First time on this website, click here |
Introduction
- Course description and requirements
- Scope and Sequence
- Proposed CourseText
- Beacon Program (SUNY Colege Credit)
- Friday Morning Video Announcements
- Required Audio & Video Projects
- Instructional Video
- Commercial
- 2 Camera Interview
- Audio Project
- Foley Project
- Documentary / PSA
Video Production Process
- Pre-Production
- Pre-production is the planning phase of the video production process. It is important to develop a clear and meaningful topic through research and writing.
- Pre-Production Writing
- Correlation between the Writing Process & The Video Production Process
- Writing a News Story
- What is News?
- Finding News Stories
- Research Your Topic
- How do you research and check facts for news?

- If interviews are planned, students will need to research each subject thoroughly before developing their questions.
- If interviews are planned, students will need to research each subject thoroughly before developing their questions.
- How do you research and check facts for news?
- Writing Concisely
- What's happening?
- Who is involved?
- Where is this happening?
- When is it happening?
- Why is it happening?
- How do you write a news script?

- Clear - use simple language
- Concise - keep sentences short
- Correct - check your facts, grammar and punctuation
-
Writing for TV, Radio and Online
- MOST IMPORTANT: Check your facts
- Think about how scripts might be different, depending on the platform they are using.
- TV - Students will need to think about the pictures - what shots would illustrate their reports? They don't need to write about what they see as people can see it? Willl students include a piece-to-camera?
- Radio - Think about using many more describing words so students can paint a picture for the people who are listening. What sounds would help their audience understand what is going on - eg: a ringing phone.
- Online - Get most of the crucial information in the top four paragraphs. What pictures would they use to illustrate the report?
- TV - Students will need to think about the pictures - what shots would illustrate their reports? They don't need to write about what they see as people can see it? Willl students include a piece-to-camera?
- MOST IMPORTANT: Check your facts
- Scripting for Film and Video Productions (Screenplay)
- A script is a text-based planning document that can be used as a stand-alone document or in conjunction with a storyboard as needed. If used as a stand-alone document, it should include descriptions of the specific shots and other visual elements, as well as the dialogue and other audio.
- Structure of a Screenplay
 Library Commercial
Library Commercial
- Suggestions for writing a Screenplay
- A script is a text-based planning document that can be used as a stand-alone document or in conjunction with a storyboard as needed. If used as a stand-alone document, it should include descriptions of the specific shots and other visual elements, as well as the dialogue and other audio.
Look at this information about a new study into children and their use of mobile phones. Pick out what you think are the most important points and then write a short script (of no more than five sentences) explaining what the story is about
Remember to cover the 5 W's:
- Correlation between the Writing Process & The Video Production Process
- Planning the Project
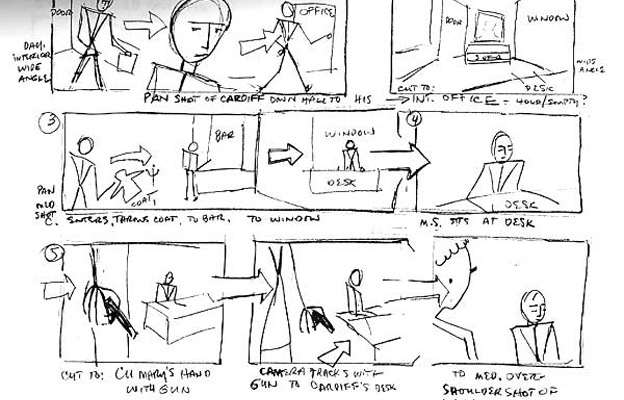
- Storyboarding
- Storyboarding is a great way to visualize how a story will be told. A basic storyboard resembles a comic strip with audio/dialogue descriptions and pictures representing the shots in each scene as they progress over time. The drawings don't have to be complicated—stick figures will do—just some sketches that indicate what students want their audience to see in their video as they tell their story.
- Timeline for the Project:
- A timeline is a basic outline of the flow of the project and can be helpful in keeping the project moving forward. It’s a simple and easy way to keep everyone on task and working together on schedule. The timeline will be based primarily on the needs of the project as outlined in the script or storyboard.
- A timeline is a basic outline of the flow of the project and can be helpful in keeping the project moving forward. It’s a simple and easy way to keep everyone on task and working together on schedule. The timeline will be based primarily on the needs of the project as outlined in the script or storyboard.
- Checklist:

- This document lists all equipment and material needs of for a production and is especially important for on-location shoots. In creating a checklist, focus on items that you are most likely to forget to bring to the shoot such as extra batteries, duct tape, microphones, costumes, props, scripts, lighting equipment, and release forms.
- This document lists all equipment and material needs of for a production and is especially important for on-location shoots. In creating a checklist, focus on items that you are most likely to forget to bring to the shoot such as extra batteries, duct tape, microphones, costumes, props, scripts, lighting equipment, and release forms.
- Schedule the Shoot:
- The last step before the cameras start rolling is scheduling the shoot. Sometimes the schedule can be broken down into a shot list. What footage is needed, and who is responsible for getting those shots?
- When scheduling, consider shooting out of sequence to save time; this means shooting all the footage needed at each respective location and then reassembling later in post-production, according to the script. Most movies are shot out of sequence.
- Considerations
- The last step before the cameras start rolling is scheduling the shoot. Sometimes the schedule can be broken down into a shot list. What footage is needed, and who is responsible for getting those shots?
- Working with Talent
- Release Forms
- General Production Forms
- Copyright
- Intellectual Property - The products of human intelligence and creation
- What is Copyright? - The legal protection of ownership of a person's intellectual property.
- If you have "COPYRIGHT" on your original work, other people CAN'T
- Make copies of your work with out telling you and paying for them.
- Use parts, or modifications, of your work with out telling you and paying for it.
- Perform your work publicly, with out telling you and paying for it.
- Display your work publicly, with out telling you and paying for them.
- If you have "COPYRIGHT" on your original work, other people CAN'T
- Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted work.
- Public Domain - Documents or media available to the public as a whole, and therefore not subject to copyright.
- You can copy, modify, distribute, and use the images, even for commercial purposes, all without asking for permission or giving credits to the artist.
- You can copy, modify, distribute, and use the images, even for commercial purposes, all without asking for permission or giving credits to the artist.
- Fair Use - (in US copyright law) the doctrine that brief excerpts of copyright material may, under certain circumstances, be quoted verbatim for purposes such as criticism, news reporting, teaching, and research, without the need for permission from or payment to the copyright holder.
- Youtube Copyright Resources
- Production
- Technical specifications for Digital Video
- Video Production Equipment:
- The Art of telling your story with Digital Video
- Videography
- Videography vs Cinematography

- Videography Terminology
- Tips for capturing quality Video
- Video Composition Examples
- Rules of Framing and Composition

- Point of View
- Videography vs Cinematography
- Cinematography
- What is Cinematography?
- What does a Cinematographer do?
- The Cinematographer's Craft
- Camera Moves
- Shot Size
- Lighting
- Classic Lighting Techneques
- 3 Point lighting set-up
- Portrait Lighting Techniques

- A Single Light Studio Techniques (with Permission)

- Basic Video & Photographic Lighting Demonstration

- How to Photograph a Headshot with Butterfly Lighting

- Cinematic Lighting Techniques

- Lighting Suggestions
- Directional and diffused light, light intensity and how to measure it, measuring incident and reflected light, and contrast
- Shadows
- Attached and cast shadows and controlling falloff
- Color
- Additive and subtractive mixing, the color television receiver and generated colors, and color temperature and white-balancing
- Lighting Instruments
- Spotlights, floodlights, and instruments for specific tasks
- Lighting Techniques
- Operation of lights, lighting
- Lighting Design
- Classic Lighting Techneques
- Cinematography Techniques Examples
- 30 Cinematology Techniques & Tips - Listing
- 30 Cinematology Techniques & Tips - Listing and Descriptions
- Production Graphics & Animation
- Adobe Photoshop
- Adobe After Effects
- What can be done with After Effects

- Adobe After Effects vs Adobe Premiere Pro

- Creating After Effects Animations
- Templates and Resources
- What can be done with After Effects
- Audio


- History of Sound at the Movies

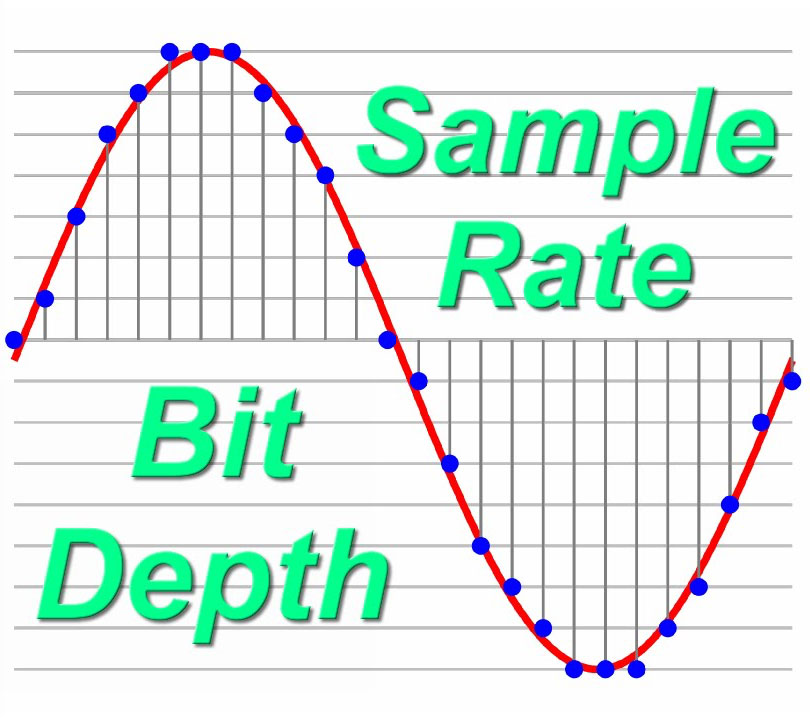
- The Science of Sound

- The Basics of Recording

- Audio Recorders for Filmmaking 2019: Choosing a Sound Recorder for Your Video Projects

- How Microphones work & types

Microphone Sound Patterns

In Studio Recordings
- History of Sound at the Movies
 Audio-Technica - Basic Audio Techneques:
Audio-Technica - Basic Audio Techneques:
- Elements of Sound Design
- Dialogue:
- Dialogue is the spoken communication between characters or individuals in a scene. It plays a vital role in storytelling, conveying information, emotions, and character development. In sound design, dialogue should be clear, intelligible, and appropriately balanced with other audio elements.
- Dialogue is the spoken communication between characters or individuals in a scene. It plays a vital role in storytelling, conveying information, emotions, and character development. In sound design, dialogue should be clear, intelligible, and appropriately balanced with other audio elements.
- Sound Effects:
- Sound effects are artificial or recorded sounds that enhance the realism and atmosphere of a scene. They can be both natural, such as footsteps, door slams, or birds chirping, and abstract, like futuristic spaceship sounds or magical spells. Sound effects are essential for creating a sense of place, heightening suspense, and emphasizing key actions or events.
- Free sound effects from Pixabay
 Free Sound Effects for Adobe Audition
Free Sound Effects for Adobe Audition
- Special Sound Effect Project (Mission Impossible Segment)
- Original Mission Impossible Segment with sound
- Mission Impossible segment without sound (download)
- Special Sound Effects Package (download)
- Sound effects are artificial or recorded sounds that enhance the realism and atmosphere of a scene. They can be both natural, such as footsteps, door slams, or birds chirping, and abstract, like futuristic spaceship sounds or magical spells. Sound effects are essential for creating a sense of place, heightening suspense, and emphasizing key actions or events.
- Music:
- Music sets the mood, evokes emotions, and enhances the narrative of a scene. It can range from subtle background melodies to powerful orchestral compositions or catchy tunes. Selecting the right music for a particular moment is crucial to create the desired impact.
- Music sets the mood, evokes emotions, and enhances the narrative of a scene. It can range from subtle background melodies to powerful orchestral compositions or catchy tunes. Selecting the right music for a particular moment is crucial to create the desired impact.
- Ambience:
- Ambience refers to the background sounds that help create a sense of place or environment. It includes natural sounds like wind, rain, or crowd chatter, as well as the acoustic characteristics of a specific location. Ambience plays a crucial role in immersing the audience in the scene, providing context, and establishing the mood.
- Ambience refers to the background sounds that help create a sense of place or environment. It includes natural sounds like wind, rain, or crowd chatter, as well as the acoustic characteristics of a specific location. Ambience plays a crucial role in immersing the audience in the scene, providing context, and establishing the mood.
- Foley:
- Foley is the art of creating and recording everyday sounds that synchronize with on-screen actions. It involves adding sounds such as footsteps, clothing rustle, or object interactions to enhance the realism and physicality of a scene. Foley artists use various props and surfaces to reproduce these sounds in sync with the visuals.
- Foley is the art of creating and recording everyday sounds that synchronize with on-screen actions. It involves adding sounds such as footsteps, clothing rustle, or object interactions to enhance the realism and physicality of a scene. Foley artists use various props and surfaces to reproduce these sounds in sync with the visuals.
- Dialogue:
- Audio Editing
On Location Recordings
- Post-Production
- Video Editing
- . Every editing software has a different set of specifications, but the basics of editing are the same regardless of the software used or the purpose of the project:
 Video Editing Example
Video Editing Example- Video Editing Fundamentals
- 10 Lessons from the Top Film Editors


 Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2018
Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2018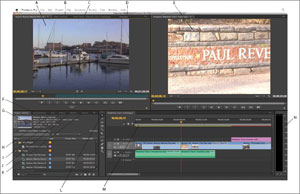
- . Every editing software has a different set of specifications, but the basics of editing are the same regardless of the software used or the purpose of the project:
- Premiere Pro Work Space
- Learning Activities
 Basic Editing Techniques
Basic Editing Techniques
- Activity #1 - Retrieving and Combining video segments

- Activity #2 - Retrieving and Combining video segments

- Activity#3 - Trimming video clips, Adjusting audio track

- Activity#4 - Trimming video clips, Adjusting audio track

- Activity#5 - Video and Audio Fade

- Activity #6 - Adding Video Transitions

- Activity #7 - Adding Text to a Video Clip

- Activity #8 - Creating Text Effects using Video Transitions

- Activity #9 - Creating the opening for a Video Broadcast

- Opening for a Video Broadcast

 Video Broadcast Files
Video Broadcast Files
- Opening for a Video Broadcast
- Activity #10 - Creating a Slide Show Video

 Activity#10 Files
Activity#10 Files- Gettysburg Address

- Activity #11 Broadcast segment
 Activity#11 Files
Activity#11 Files- Broadcast segment

 Intermediate Editing Techniques
Intermediate Editing Techniques
- Intermediate Activity #1 - Green Screen Integration

- Intermediate Activity #4 - Color Correction
- Intermediate Activity #5 - Masking
- Masks allow you to define a specific area in a video clip that you want to blur, cover, highlight, apply effects or color correct. Effects can be applied inside or outside a masked area.
- Covering a specific area Mask Activity
- Color Correction Mask
- Masks allow you to define a specific area in a video clip that you want to blur, cover, highlight, apply effects or color correct. Effects can be applied inside or outside a masked area.
- Careers in Video Production
- Production Roles
- Scriptwriter
- The scriptwriter works with the producer and the pre-production team to produce a script or screenplay for a production.
- Producer
- A producer oversees the entire production from start to finish. Responsibilities include the research and development of ideas into project proposals, supporting the creative teams, and managing the finances and production schedule. As head supervisor, the producer has the ultimate control of a production.
- Director
- The director oversees the vision of a production. He or she is the person responsible for harnessing the artistic and dramatic aspects of the script, set, talent, and technical crew to achieve the final look and feel of a production.
- The Director: Crash Course Film Production

- Cinematographer
- Cinematography is the art and craft of making motion pictures by capturing a story visually. Though, technically, cinematography is the art and the science of recording light either electronically onto an image sensor or chemically onto film.
- Taken from the Greek for "writing with movement," cinematography is the creation of images you see on screen. A series of shots that form a cohesive narrative. Cinematography composes each shot, considering, where everything in frame demands attention.
- The Cinematographer: Crash Course Film Production

- Dissecting The Camera: Crash Course Film Production

- Audio Technician
- Audio technicians are responsible for all of the sound elements in a production. The audio technician performs mic checks on the set of a production to maintain an accurate audio balance. In audio post, he or she will harmoniously incorporate natural sound, music, sound effects, and voiceover treatments into the finished product.
- Sound Production: Crash Course Film Production

- Set Design
- Literally, ‘mise-en-scene’ means “placing on stage.” But in film, mise-en-scene encompasses everything the camera is capturing. The artists and crafts-people who work in Production Design, Wardrobe, and Hair and Makeup are responsible for setting the stage of a film and making sure the characters fit on that stage. In this episode of Crash Course Film Production, Lily talks us through the roles involved in designing the world of a film.
- Designing the World of Film: Crash Course Film Production

- Lighting Design
- It's time to look at some of the most under-sung heroes of the film world, Grip and Electric. Doing everything from setting up dollies and tripods, to helping the cinematographer shape the light with flags and silks, the Grips are there to make it work properly. And when working with electricity (as pretty much ever film set does) you need experienced technicians to make sure you are doing it safely and that you'll have the power you'll need. Which is where the Electric department comes in.
- Grip and Electric: Crash Course Film Production

- Special Effects
- Chances are, when you hear the phrase "Special Effects," you may have images pop into your mind. The Hulk smashing a city, a lightsaber fight, or maybe an alien world. But effects can be much more subtle and have been around really since the beginning of filmmaking. In this episode of Crash Course Film Production, Lily Gladstone talks about the basics of special effects.
- Special Effects: Crash Course Film Production

- Editor
- The editor works with the producer and director to assemble and polish the finished program, using video and audio captured during the production phase.
- The Editor: Crash Course Film Production

- Film School or Not
- Should you go to film school? Great question? But there aren't necessarily a lot of direct answers. Do you want to go to Hollywood? Do you want to make movies in your spare time? Do you want to learn about world cinema? Do you want to be a director? A cinematographer? An editor? Do you want to pay for tuition? All of these questions can help you figure it out, but today Lily Gladstone will talk us through a few important things to keep in mind when deciding if film school may be right for you!
- To Film School or Not To Film School: Crash Course Film Production

- Film School or Not
- Should you go to film school? Great question? But there aren't necessarily a lot of direct answers. Do you want to go to Hollywood? Do you want to make movies in your spare time? Do you want to learn about world cinema? Do you want to be a director? A cinematographer? An editor? Do you want to pay for tuition? All of these questions can help you figure it out, but today Lily Gladstone will talk us through a few important things to keep in mind when deciding if film school may be right for you!
- To Film School or Not To Film School: Crash Course Film Production

- Television Production
- In our final episode of Crash Course Film Production, it's time to take a look at television production and how it differs from feature film production. It's subtle but it has a lot to do with how television shows make money for their many different types of platforms. So, strap in and get ready for a trip into the world of TV!
- Television Production: Crash Course Film Production

- Where do I go from here?: Local College Programs
Additional Video Production & Cinematography Resources
| Design & Drawing | Electricity / Electronics | Digital Photography 1 | Digital Photography 2 | Video Production |